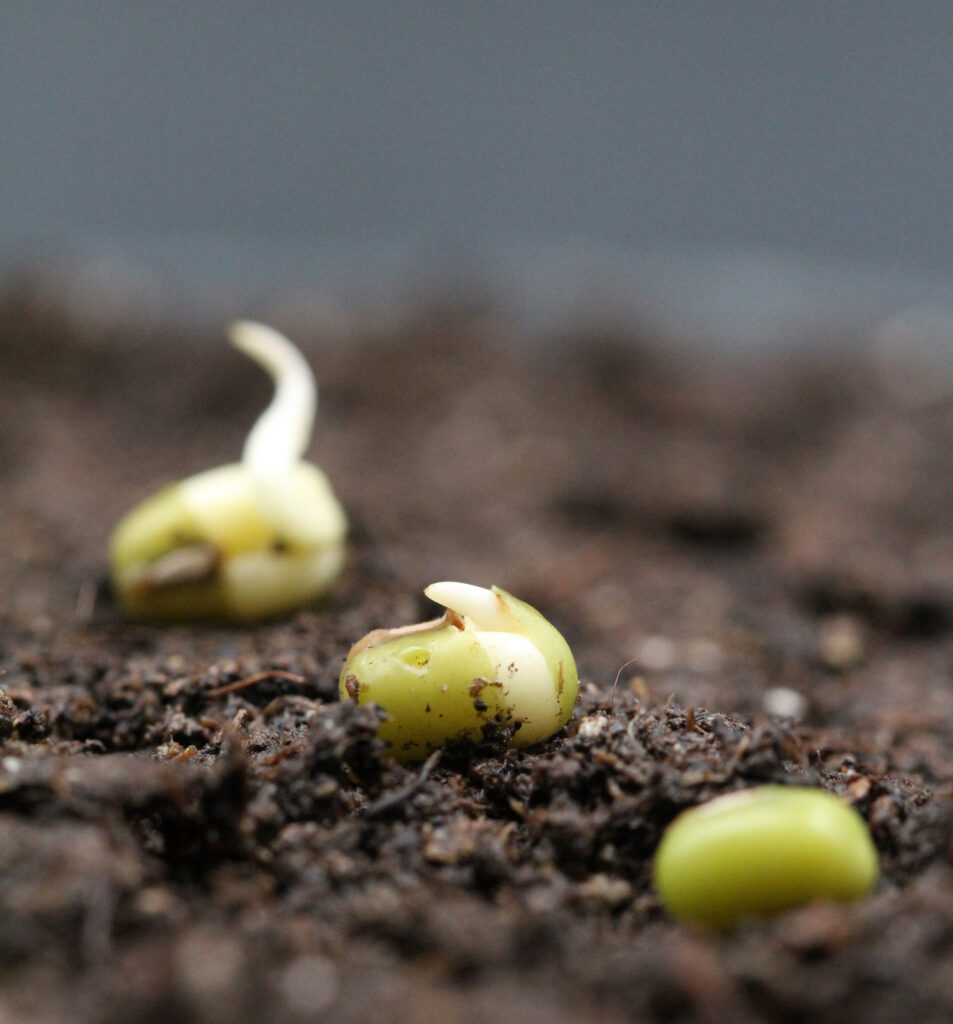

Once in life we all do the experiment of sprouting the seeds. By soaking the seeds and sprouting it in cotton bag, but we all somewhere fail in it to grow perfect sprouts.
In this blog we understand the science behind Sprouting and how we can grow the sprouts perfectly
What is sprout?
Sprout is a young plant shoot, the sprouts is develop during the process of germination, when we soak , drain and keep that seed in specific environmental condition the seed start to germinate which results in formation of sprouts.
What is germination?
In simple language the germination is process in which seeds start to develop in new plant this growth starts from the seed embryo under the favourable condition
The condition require for proper seed germination –
- Water-
To activate the seed germination process water plays a very important role, the amount of water for soaking depends on dry matter of seeds . Water makes the seed coats soft and enhances the seed permeability, as seed is permeable the dissolve oxygen in water easily accessible to seed embryo. Water also helps to solubilise insoluble food to seed embryo
- Temperature-
Seed germination is complex process within the seeds it involves enzymes, hormones, moisture migration to accelerate this all reactions need suitable temperature
The require temperature is vary from plant to plant but mostly it is (25 to 30 ⁰c)
- Oxygen-
During the germination process seeds are continuously in stage of respiration also they need energy as well, both of this requirement is fulfil by the oxygen and its utilisation
- Light-
We all Know how the plant produces there food by the photosynthesis that’s why the light is require for germination process
Understand seed structure and its part-
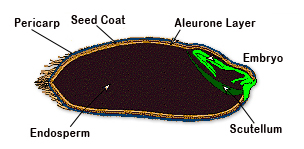
A seed is fertilized, matured ovule of a flowering plant, containing an embryo, Seeds are protected by its hard coating they are in dormant stage until they get proper condition for their growth
Part of seed are as below
Embryo
Endosperm
Seed coat
Aleurone layer
Pericarp
- Embryo-
Embryo is part of seed that grows into entire plant
- Endosperm-
Endosperm located below the seed coat, the endosperm is storage house of nutrients, starch, carbohydrate and proteins, which act as energy source for the embryo during the process of germination
- Seed coat-
The seed coat as a shield for the endosperm and embryo, it also protect them from unfavorable environmental condition such as direct sunlight, parasites, water.
- Aleurone layer-
The aleurone layer is the outermost layer of the endosperm, followed by the inner starchy endosperm. Aleurone is especially rich in protein
- Pericarp-
Pericarp is divided into three layer one protect the fruit skin that is epicarp , one is flesh that is mesocarp , and one protects the seed is endocarp
What are changes done in seed during sprouting-
As water is absorb by the seed germination process start , Hydrolytic enzymes activate and start showing there activity they breakdown the starch present in endosperm in simple carbohydrate for nourishing the embryo.
Also the enzymes are produced in the aleurone layer in response to gibberellins (hormones) produced in the scutellum. Carbohydrates from the endosperm are absorbed by the scutellum and transmitted to other parts of the embryo.
As embryo start developing it first develops into the radicle and plumule
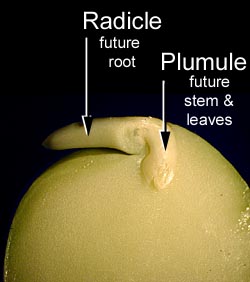
Radicle-During the sprouting the first portion forms i.e. radicle the radicle seems to be the plant’s embryo stem, which develops downwards in the earth we call it root of the plant
Plumule- A plumule seems to be the portion of the embryo that grows into the stalk that bears the soil’s first genuine leaves further it rises to several leaves, branches, flowers, and seeds.
What is ideal process and condition of sprouting?
How to make sprouts at home fast or How to make sprouts step by step ?
- Soak the seeds for about 8 to 12 hrs in 25 ⁰c ±2 water
- After complete soaking time rinse the water and allow them to drain properly for 1-2 hr
- As water is completely drain out again wash it with water and shift it to your sprouting jar or tie it in wet cotton.
Why wet cotton- because it provides the moisture require for sprouting you have to wet it in intervals of 3-4 hrs. and other reason is as germination is in process it produces heat during this reaction and we are using the cotton which helps to pass heat out of it and maintain the proper environmental condition for sprouting
4.Sprouts will be ready within 1-2 days , It depends on the type of seed
5.Surface Dry it completely and store in fridge
6.The shelf life is around 4-5 days
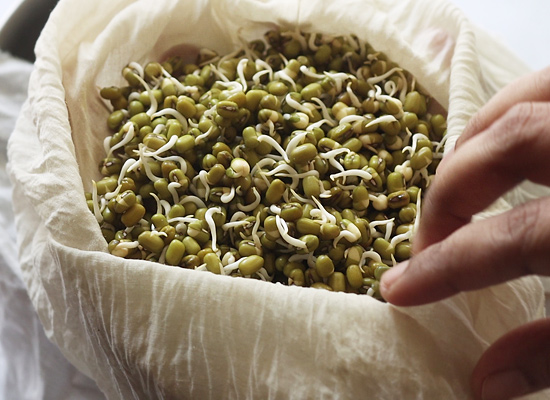

Benefits of eating sprouts-
Most of seeds have indigestible properties, many of them contain anti- nutrients substances that inhibit the absorption or use of other nutrients in the body
For example –Phytate and polyphenols are present in legumes but sprouting helps to reduce this anti-nutrients
Various pre-treatment methods exist to avoid such issues with seeds and can be used to enhance the bioavailability of nutrients, including soaking, fermentation and sprouting
1. Sprouting enhances the bioavailability of zinc, iron and calcium
2. Proteins are easily digestible because for the germination the enzyme degrade the complex protein in its simpler form which are ready available in sprouts
3. Sprouting increases the vitamins and mineral content
4. B complex vitamin increases 5-10 times more
5. Level of Vitamin C increases
6. As the anti-nutritional factors reduce by sprouting it is easy to digest
7. Sprouts also have a lot of dietary fiber and negligible amount of calories which helps regulates digestion and weight loss